The Ultimate Guide to the Vegan Diet: Benefits, Risks, and Tips
Introduction
The vegan diet, focused on plant-based foods, excludes all animal products, including dairy, eggs, and honey. This comprehensive guide explores the benefits, risks, and practical tips for following a vegan diet, providing insights into how it can improve your health and support the environment.
What Is a Vegan Diet?
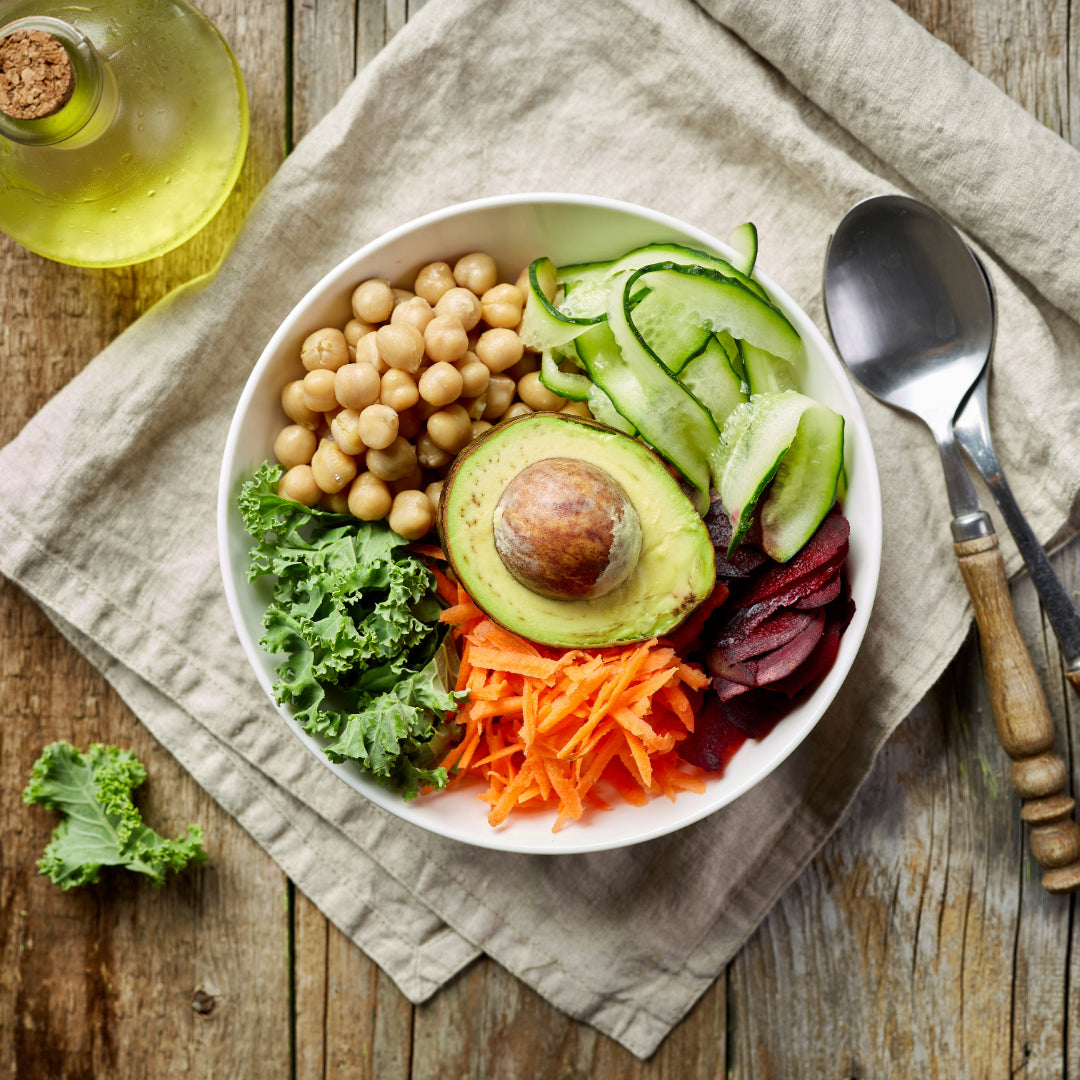
A vegan diet includes only plant foods—fruits, vegetables, beans, grains, nuts, and seeds. People who follow a vegan diet don't eat any animal foods, including dairy, eggs, and honey. About 3% of Americans follow a vegan diet for various reasons, including health, ethical, and environmental concerns.
Vegan vs. Vegetarian
While both vegans and vegetarians avoid meat, vegans also exclude all animal products, including dairy, eggs, and honey. Vegetarians may consume these products.
Types of Vegan Diets
Raw Vegan Diet
Raw vegans eat only raw plant foods, believing that cooking reduces nutritional value. This diet includes uncooked fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, and fermented foods.
Vegan Keto Diet
The vegan keto diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet, focusing on high-fat vegan foods like avocados, nuts, and seeds, while restricting grains, starchy vegetables, and high-sugar fruits.
Vegan Diabetic Diet
This diet is low in high-glycemic carbs and focuses on whole grains, beans, legumes, and high-fiber foods to help control blood sugar.
High-Protein Vegan Diet
A high-protein vegan diet emphasizes higher-protein plant foods such as nuts, seeds, beans, tofu, quinoa, seitan, and oats, often supplemented with vegan protein powders.
Alkaline Vegan Diet
This diet prioritizes foods based on their pH value, promoting alkaline foods like fruits, non-starchy vegetables, and whole grains while avoiding acidic foods.
Vegan Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Balanced vegan diets naturally reduce inflammation by focusing on fresh, whole foods and limiting sugars and highly processed foods.
Mediterranean Vegan Diet
A vegan adaptation of the Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, beans, nuts, seeds, and unsaturated oils, but excluding fish, dairy, and eggs.
Low-Carb Vegan Diet
This diet includes low-carb plant foods like non-starchy vegetables, high-fat fruits, nuts, seeds, and soy products.
Vegan Food List
On a vegan diet, you can eat foods made from plants, including:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Legumes such as peas, beans, and lentils
- Nuts and seeds
- Breads, rice, and pasta
- Vegetable oils
You can eat them whole or in prepared or processed foods like tofu, seitan, tempeh, vegan meats, plant-based milks, and vegan cheese.
Foods That Aren't Vegan
Vegans don't eat any foods made from animals, including:
- Beef, pork, lamb, and other red meat
- Chicken, duck, and other poultry
- Fish or shellfish
- Eggs
- Cheese
- Butter
- Milk, cream, ice cream, and other dairy products
- Mayonnaise (because it includes egg yolks)
- Honey
Getting the Right Nutrients from a Vegan Diet
With good planning and an understanding of what makes up a healthy, balanced vegan diet, you can get all the nutrients your body needs. Key nutrients to focus on include:
Vegan Sources of Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium is needed for healthy bones and teeth. Good vegan sources include green leafy vegetables, fortified unsweetened soya, pea and oat drinks, calcium-set tofu, sesame seeds, tahini, pulses, and dried fruit. For vitamin D, consider exposure to sunlight, fortified foods, and supplements.
Vegan Sources of Iron
Iron is essential for red blood cell production. Good sources for vegans include pulses, wholemeal bread and flour, fortified breakfast cereals, dark green leafy vegetables, nuts, and dried fruits.
Vegan Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is crucial for healthy blood and nervous system. Vegan sources include fortified breakfast cereals, unsweetened soya drinks, yeast extract, and nutritional yeast flakes. A B12 supplement may be necessary.
Vegan Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for heart health. Vegan sources include ground linseed, chia seeds, shelled hemp seeds, walnuts, and vegetable oils.
Vegan Nutrition
A well-planned vegan diet can provide all the nutrients you need. Focus on variety and include foods high in calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Veganism Benefits
Research has shown that plant-based diets can improve your health and reduce the risk of many diseases. Benefits include:
- Lower risk of type 2 diabetes
- Reduced risk of prostate cancer
- Lower risk of cardiovascular disease
- Better weight management
Vegan diets are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and tend to be lower in unhealthy saturated fat and cholesterol.
Vegan Diet Risks
While a vegan diet can be very nutritious, it can also shortchange you on certain nutrients, such as protein, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, vitamin B12, and vitamin D. These nutrients are especially important for children's growing bodies and during pregnancy. A well-planned diet is crucial to avoid deficiencies.
Vegan Supplements
While a balanced vegan diet can provide all necessary nutrients, supplements may be helpful in certain situations. For example, highly active people may need extra protein, and a B12 supplement may be necessary for those who don't consume fortified foods.
Vegan Diet and Pregnancy
It's safe to eat```html a vegan diet during pregnancy, but it's important to ensure you get enough key nutrients for your and your baby's health. These nutrients include iron, vitamin B12, calcium, protein, vitamin D, and iodine. Folate (or folic acid) is also essential during pregnancy. Here are some sources:
- Fortified cereals, bread, and pasta
- Peanuts
- Leafy green vegetables
- Orange juice
- Beans
Your doctor may recommend a folic acid supplement and other supplements if you're unable to meet your nutritional needs through diet alone.
Vegan and Breastfeeding
The same balanced diet you follow during pregnancy will provide the nutrients you need while nursing. One review study found no difference in the nutritional quality of breast milk among non-vegetarians, vegetarians, and vegans.
How to Go Vegan
If you're interested in adopting a vegan diet, you can either make the transition gradually or dive in all at once. Here are some tips for getting started:
- Gradual Transition: Start by increasing the amount of fruits and vegetables at each meal and gradually cut out meat, dairy, and eggs.
- Find Substitutes: Use plant-based substitutes for your favorite animal products, like almond milk for dairy milk or tofu for chicken.
- Plan Your Meals: Create a meal plan that includes a variety of vegan foods to ensure you get all necessary nutrients.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the nutritional needs of a vegan diet and how to meet them through food and supplements if needed.
- Seek Support: Join vegan communities online or in person for support and advice.
If removing all animal products from your diet feels overwhelming, consider a less strict approach:
- Pescatarian: No meat and poultry, but you can still eat fish.
- Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian: Plant-based diet plus dairy and eggs.
- Flexitarian: Plant-based diet that occasionally includes animal products.
Consult your doctor or a dietitian to help you choose the right foods as you start a vegetarian or vegan diet, especially if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Conclusion
The vegan diet offers numerous benefits, including improved health, weight management, and environmental sustainability. However, it's crucial to plan your diet carefully to ensure you get all the necessary nutrients. Whether you choose to go fully vegan or take a more gradual approach, make sure to educate yourself, seek support, and consult with healthcare professionals to make the transition smooth and successful.
How We Reviewed This Article
Our content is based on thorough research and evidence from reputable sources to provide you with the most accurate and reliable information.
Evidence-Based
All claims and recommendations in this article are supported by scientific studies and expert opinions.